Void-form concrete slabs, also known as voided or bubble deck slabs, represent a transformative innovation in the construction industry. This article delves into the concept, advantages, design considerations, and applications of void-form concrete slabs, shedding light on how this innovative approach is redefining the way we think about structural efficiency and sustainability in building design.
Introduction to Void Form Concrete Slabs:
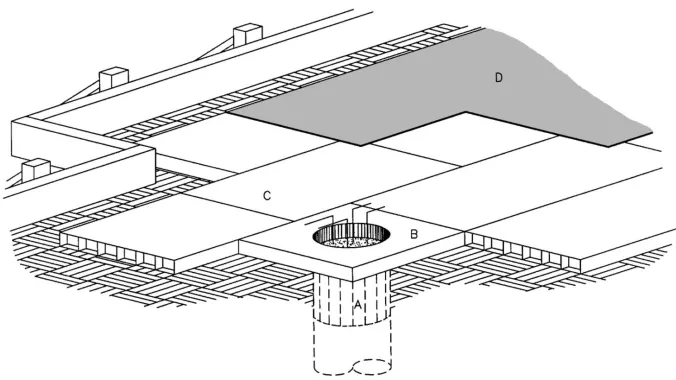
Void-form concrete slabs depart from traditional solid concrete slabs by incorporating hollow spaces or voids within the structure. These voids are created using preformed elements, such as plastic or foam spheres, which are strategically placed within the concrete during the casting process. The result is a slab that maintains structural integrity while significantly reducing its overall weight.
Advantages of Void Form Concrete Slabs:
Reduced Dead Load: One of the primary advantages of void-form concrete slabs is the reduction in dead load. The incorporation of hollow spaces decreases the amount of concrete required, leading to lighter structures. This is particularly beneficial in high-rise buildings, where dead load reduction can contribute to overall structural efficiency.
Improved Structural Efficiency: Void form slabs optimize the distribution of materials, enhancing structural efficiency. The reduced weight allows for longer spans and increased flexibility in architectural design, providing more freedom to architects and designers.
Material Conservation: By using less concrete without compromising structural strength, void-form slabs contribute to material conservation. This aligns with sustainable construction practices, as it minimizes the environmental impact associated with the production and transportation of excess concrete.
Thermal Insulation: The voids in the slab can be filled with insulating materials, enhancing the thermal performance of the structure. This feature is particularly valuable in regions with extreme temperatures, contributing to energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
Construction Speed: Void form slabs often lead to faster construction times. The reduced weight facilitates easier handling and installation, allowing for quicker assembly on the construction site.
Design Considerations:
Void Placement: The strategic placement of voids within the slab is a critical design consideration. Engineers and architects work together to determine the optimal location of voids to ensure that structural integrity is maintained while achieving the desired weight reduction.
Load-Bearing Capacity: The load-bearing capacity of void form slabs is carefully calculated to meet the specific requirements of the building. Engineers consider factors such as live loads, dead loads, and dynamic loads to determine the appropriate design for the structure.
Material Compatibility: The materials used for the void forms must be compatible with concrete and capable of withstanding the casting process and subsequent loads. Common void-form materials include plastic or foam spheres that are strong enough to support the weight of wet concrete.
Insulation Options: When incorporating voids for thermal insulation, designers can choose from a variety of insulating materials. This includes foam boards, lightweight aggregates, or other materials with low thermal conductivity.
Applications of Void Form Concrete Slabs:
High-Rise Buildings: Void form slabs are particularly well-suited for high-rise buildings where the reduction of dead load is critical for structural efficiency. The lighter weight allows for taller structures without compromising safety.
Commercial Construction: In commercial construction, void form slabs are gaining popularity for their speed of construction and sustainability benefits. Large-span structures, such as shopping malls or office complexes, can benefit from the reduced weight and improved efficiency of void-form slabs.
Residential Construction: Void form slabs can also be applied in residential construction, offering homeowners the advantages of energy-efficient and environmentally friendly building solutions. The reduced weight can be especially beneficial in areas with poor soil conditions.
Infrastructure Projects: Infrastructure projects, such as bridges and overpasses, can benefit from the reduced dead load and improved structural efficiency provided by void-form concrete slabs. The lightweight nature of these slabs simplifies transportation and installation.
Sustainability Considerations:
Material Reduction: Void form concrete slabs contribute to sustainability by reducing the overall material usage in construction. This results in less concrete production, lowering the carbon footprint associated with cement manufacturing.
Energy Efficiency: The thermal insulation capabilities of void form slabs contribute to improved energy efficiency in buildings. Reduced energy consumption for heating and cooling aligns with sustainable building practices.
Long-Term Durability: The structural efficiency of void form slabs can contribute to the long-term durability of buildings, reducing the need for extensive maintenance and repair over the lifespan of the structure.
Waste Reduction: By optimizing the use of materials, void form slabs minimize construction waste, promoting responsible and sustainable construction practices.
Conclusion:
Void-form concrete slabs represent a paradigm shift in construction methodology, offering a compelling blend of structural efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and design flexibility. As the construction industry continues to prioritize sustainability and innovative building solutions, void-form slabs are poised to become an increasingly integral component of modern architectural design. With their advantages in weight reduction, improved thermal performance, and accelerated construction times, void-form concrete slabs exemplify the industry’s commitment to advancing both efficiency and sustainability in the built environment.