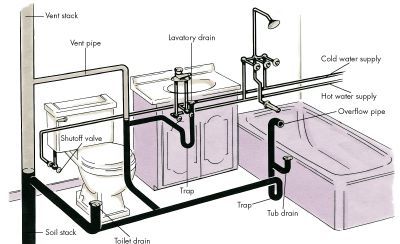
Embarking on a bathroom renovation or plumbing project? Understanding the intricacies of a bathroom plumbing diagram is paramount to ensuring a well-functioning and efficient plumbing system. This comprehensive guide will unravel the mysteries of bathroom plumbing, covering key components, configurations, and installation considerations.
Components of a Bathroom Plumbing Diagram
Supply Lines
At the heart of any bathroom plumbing diagram are the supply lines. These pipes deliver hot and cold water to various fixtures, such as sinks, showers, and bathtubs. Proper sizing and layout of supply lines are crucial to ensure consistent water pressure and temperature throughout the bathroom.
Drain-Waste-Vent (DWV) System
The DWV system is the backbone of the drainage system in a bathroom. It includes drainpipes that carry wastewater away from fixtures, waste pipes that transport solid waste, and vent pipes that allow air to enter the plumbing system, preventing suction and ensuring smooth drainage.
Fixtures and Appliances
Each fixture and appliance in the bathroom, including sinks, toilets, showers, and bathtubs, is connected to the plumbing system through specific pipes. Understanding the connections and pathways of these pipes in the bathroom plumbing diagram is essential for proper installation and maintenance.
Bathroom Plumbing Configurations
Single-Stack System
In a single-stack system, a single vertical stack serves as the main drainage conduit for all fixtures in the bathroom. While simpler in design, this configuration requires careful planning to ensure adequate venting and efficient drainage.
Wet Venting
Wet venting is a configuration where one drain pipe serves multiple fixtures, with the vent pipe running alongside. This space-saving design is common in bathrooms where fixtures are in close proximity, optimizing both space and plumbing efficiency.
Installation Guidelines
Proper Sloping
Ensuring proper slope in drainpipes is crucial to facilitate the smooth flow of wastewater. Drainpipes should have a gradual slope to prevent water and waste from pooling, promoting efficient drainage and preventing clogs.
Venting Considerations
Vent pipes play a crucial role in preventing sewer gases from entering the bathroom and ensuring optimal drainage. Proper venting considerations, including vent pipe size and placement, are essential for the overall functionality of the plumbing system.
Fixture Placement
Strategic placement of fixtures in the bathroom plumbing diagram is essential for efficient plumbing. Placing fixtures in close proximity can reduce the need for extensive piping and venting, streamlining the plumbing system and minimizing installation costs.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Clogs and Blockages
Common issues in bathroom plumbing include clogs and blockages. Understanding the flow pathways in the plumbing diagram can aid in identifying and clearing blockages efficiently.
Venting Problems
Inadequate venting can lead to slow drainage, gurgling sounds, and unpleasant odors. Troubleshooting venting problems requires a careful examination of the plumbing diagram to identify and address vent pipe issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a well-designed bathroom plumbing diagram is the blueprint for a functional and efficient plumbing system. Whether you’re embarking on a new construction project or tackling a renovation, understanding the components, configurations, and installation guidelines outlined in the plumbing diagram is essential. Navigate the pipes with confidence, and ensure your bathroom plumbing operates seamlessly for years to come.