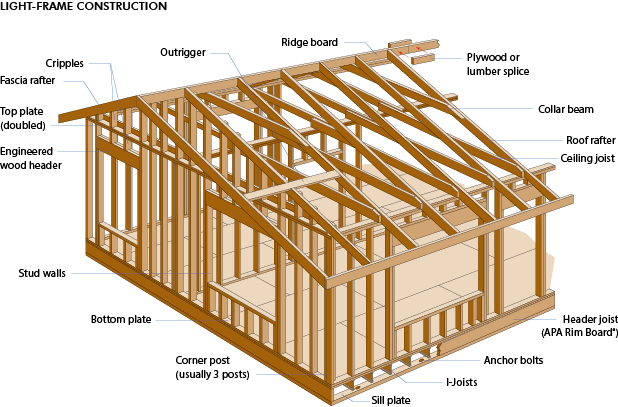
Wood light frame construction, also known as platform framing, is a popular method of construction for residential and commercial buildings in North America. This construction method is based on the use of lumber for framing, which is cut into standardized sizes and assembled into walls, floors, and roofs using a systematic process. In this article, we will explore some of the key aspects of wood light-frame construction.
Framing Members
The basic framing members in wood light-frame construction are studs, plates, headers, and joists. These members are made from dimensional lumber, typically 2×4 or 2×6 in size, and are cut to the required length for each wall, floor, or roof section. Studs are vertical members used to frame walls, while plates are horizontal members used to attach the studs and provide a surface for floor and roof framing. Headers are used to span openings such as doors and windows, and joists are used to support floors and roofs.
Sheathing
The sheathing is the material used to cover the exterior walls, floors, and roofs of the building. In wood-light frame construction, sheathing is typically made of plywood or oriented strand board (OSB). The sheathing is attached to the framing members using nails or screws, providing rigidity and strength to the structure.
Insulation
Is an important component in wood light frame construction, as it helps to reduce heat loss and gain, improve energy efficiency, and provide acoustic benefits. Insulation is typically installed between the framing members, in the walls, floors, and roofs of the building. The most common insulation materials used in wood light-frame construction are fiberglass batts, blown-in cellulose, and spray foam.
Mechanical and Electrical Systems
Mechanical and electrical systems are an essential part of any building, and wood-light-frame construction is no exception. In order to accommodate these systems, openings are made in the sheathing and framing for pipes, ducts, and wiring. The placement of these openings is carefully planned during the design process to ensure that they do not interfere with the structural integrity of the building.
Fire Protection
Fire protection is an important consideration in wood light frames, as wood is a combustible material. protection measures include the use of fire-resistant materials such as gypsum board for interior walls and ceilings and the installation of fire-rated doors and windows. In addition, fire sprinklers and smoke alarms are often installed to provide early warning and suppression in case of a fire.
Structural Design
The structural design of wood light- is based on a system of load-bearing walls and floors, which transfer the weight of the building to the foundation. The design of the framing members, sheathing, and connections is carefully engineered to ensure that the building can withstand the forces of gravity, wind, and seismic activity.
Environmental Considerations
Wood light frame is considered to be a sustainable and environmentally friendly building method, as it uses a renewable resource and has a lower carbon footprint than other construction methods. In addition, wood is a natural insulator, which can help to reduce energy consumption and improve indoor air quality.
Advantages
The wood light frame offers several advantages over other construction methods. It is relatively quick and easy to construct and can be customized to suit a wide range of building designs and sizes. In addition, wood is a readily available and affordable building material. And wood light-frame is typically less expensive than other methods such as masonry or steel frame construction.
Disadvantages
Despite its advantages, wood light frame also has some disadvantages. Wood is a combustible material, which means that it is more susceptible to fire than other building materials. In addition, wood is prone to rot and decay if it is exposed to
moisture for extended periods of time, which can compromise the structural integrity of the building. To mitigate these risks, proper fire protection measures and moisture management strategies. Must be employed during construction and throughout the life of the building.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and safety of wood-light-frame buildings. This includes routine inspections for signs of rot, decay, and termite damage. As well as maintenance of the exterior finishes such as paint or stain. Proper ventilation and moisture management strategies are also important for preventing moisture damage and prolonging the life of the building.
In conclusion, the wood light frame is a popular and versatile method of construction. That offers many benefits including affordability, sustainability, and customization. However, it also has some inherent risks and requires proper planning, design, and maintenance to ensure safety and longevity. If you are considering wood-light-frame for your building project. It is important to work with experienced professionals who can guide you through. The process and help you make informed decisions.